nf-core/radseq
Variant-calling pipeline for Restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (RADseq).
Introduction
This document describes the output produced by the pipeline. Most of the plots are taken from the MultiQC report, which summarises results at the end of the pipeline.
The directories listed below will be created in the results directory after the pipeline has finished. All paths are relative to the top-level results directory.
Pipeline overview
The pipeline is built using Nextflow and processes data using the following steps:
- Preprocessing
- FastP - trim low-quality reads, umi-barcodes, adapters
- Denovo Reference Construction
- Prepare forward reads - combine forward and reverse sequences separated by ‘NNNNNNNNNN’
- Combine uniqe reads - retain reads present n number of times between and across individuals
- Seqtk - write dummy fasta file
- Denovo FastP - trim adapters
- CD-HIT-EST - cluster similar sequences
- CD-HIT-EST to Rainbow div - convert cdhit file output into rainbow div input file format
- Rainbow div - distiguish sequence errors from heterozygote or variants between repetitive sequences
- Rainbow merge - merge potential heterozygous clusters
- Write Fasta - convert rainbow merge file output into fasta format
- Alignment
- SAMtools - Sort, index and obtain alignment statistics
- BWA - short read aligner
- BWAMEM2 - a faster short read aligner
- UMI-tools dedup - UMI-based deduplication
- Freebayes Intervals
- BEDtools bamtobed: converts bam file into bed datastructure
- BEDOPS merge: merge indvidual bed files into a single bed file
- BEDtools sort: sorts bed files
- BEDtools coverage: counts read depth
- BEDtools merge: merges indv bed files and takes sum the read depths
- BEDtools makewindows: split regions with coverage above
--max_read_coverage_to_splitto half read length - BEDtools intersect: removes any overlapping regions between split reads and all merged reads
- Create intervals: write regions for input to
freebayes
- Variant Calling
- FreeBayes - a bayesian genotyper tool
- Quality Control and Preprocessing
- FastQC - Raw read QC
- MultiQC - Aggregate report describing results and QC from the whole pipeline
- Pipeline information - Report metrics generated during the workflow execution
Directory Structure
The default directory structure is as follows. This includes output from both denovo and reference methods.
{outdir}
├── denovo
│ ├── alignments
│ │ └── bwamem2
│ │ ├── bam
│ │ ├── index
│ │ ├── intervals
│ │ │ ├── bedops_merge
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_bamtobed
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_coverage
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_intersect
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_makewindows
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_merge
│ │ │ ├── bedtools_sort
│ │ │ └── create_intervals
│ │ ├── samtools_index
│ │ ├── samtools_merge
│ │ ├── samtools_stats
│ │ └── umitools_dedup
│ │ └── stats
│ ├── reference
│ │ ├── cdhit
│ │ ├── cdhit_to_rbdiv
│ │ ├── fastp
│ │ ├── rainbow_div
│ │ ├── rainbow_merge
│ │ ├── samtools
│ │ │ └── index
│ │ ├── seqtk
│ │ ├── unique_sequences
│ │ └── write_fasta
│ ├── trim_fastp
│ └── variant_calling
│ └── intervals
├── fastp
├── fastqc
├── multiqc
│ └── multiqc_data
├── pipeline_info
└── reference
├── alignments
│ └── bwamem2
│ ├── bam
│ ├── index
│ ├── intervals
│ │ ├── bedops_merge
│ │ ├── bedtools_bamtobed
│ │ ├── bedtools_coverage
│ │ ├── bedtools_intersect
│ │ ├── bedtools_makewindows
│ │ ├── bedtools_merge
│ │ ├── bedtools_sort
│ │ └── create_intervals
│ ├── samtools_index
│ ├── samtools_merge
│ ├── samtools_stats
│ └── umitools_dedup
│ └── stats
├── samtools
│ └── index
└── variant_calling
└── intervalsPre-Processing
Radseq pre-processes reads prior to the alignment step.
FastP
FastP is a tool designed to be an all-in-one preprocessor for FastQ files. You can enable the saving of trimmed fq files in output directory through --save_trimmed=true.
Output files
{outdir}/fastp/*.fq.gz: trimmed fq files
Denovo Reference Construction
Radseq supports the construction of psuedoreference using a conglomerate of open source tools. By default the resulting fasta file is only outputed to enable the printing of intermediate files into {outdir}/denovo/reference/ use --denovo_intermediate_files=true.
Prepare forward reads
Prior to clustering forward and reverse reads are joined into one sequence and seperated with a NNNNNNNNNN. Reads are reduced based on number of presences within an individual and among all individuals and combined into one file.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/unique_sequences*.uniq.seqs: all unique sequences in an individual*_uniq.full.fasta: all sequences
Seqtk seq
Seqtk is a tool for processing FASTA or FASTQ file formats.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/seqtk*.seqtk-seq: dummy fasta file
Denovo FastP
Denovo Fastp uses FastP as a tool to trim any unwanted sequences prior to clustering like adapter content.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/fastp*.uniq.fasta: fasta format*.totaluniqseq: all unique sequences remaining after data cutoffs and adapter trimming
Cdhit est
CD-HIT is used for clustering and comparing nucleotide sequences.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/cdhit*_cdhit.logs: log output from cdhit-est*.clstr: clstr output used to convert into rainbow div format
CD-HIT to Rainbow div
This module converts CD-HIT output into input for Rainbow div.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/cdhit_to_rbdiv*.sort.contig.cluster.ids: intermediate file used for conversion ofcd-hittoRainbowinput and facilitates reproducibility*.contig.cluster.totaluniqseq: used during assembly*.rcluster: input forRainbow
Rainbow div
Rainbow div is a tool used to divide heterozygote calls into putative haplotypes based on minimum thresholds passed as arguments.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/rainbow_div*_rbdiv.out: rainbow div output file*_rbdiv.log: log file
Rainbow merge
Rainbow merge is a tool used to merge reads from Rainbow div and assemble into contigs based on minimum and maximum thresholds that are passed as arguments.
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/rainbow_merge*_rainbow.fasta: final fasta file used in subsequent processes
Write fasta
This module converts Rainbow merge into fasta format. These files are outputed by default to:
Output files
{outdir}/denovo/reference/write_fasta*_rainbow.fasta: denovo fasta file containing contig sequences
Alignment
Indices
enable the saving of reference indices with --save_reference_indices true generate from samtools and bwa for variant calling and short-read alignment respectiviely.
samtools faidx
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/reference/{samtools}/index/*.fai: samtools fai index
bwa index
Not Working
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/reference/{aligner}/index/*: rainbow merge output file
Aligners
To enable the output of bam files use --save_bam_files=true. Output of bam files from different alignment methods follow the same output structure.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/reference/{aligner}/bam/*.bam: sorted bam files
BWA
BWA is a tool for mapping sequencies with low divergence against a reference genome. Aligned reads are then potentially filtered and coordinate-sorted using samtools.
BWA-mem2
BWA-mem2 is a tool next version of bwa-mem for mapping sequencies with low divergence against a reference genome with increased processing speed (~1.3-3.1x). Aligned reads are then potentially filtered and coordinate-sorted using samtools.
UMI-tools dedup
UMI-tools dedup is a tool for deduplicating reads and ensuring only a single representative read is retained in the bam file. Files are outputed using --save_bam_files=true as a result of many individual bed files being passed through.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/umitools_dedup*.bam: bam file*.tsv: output statistics file
FreeBayes Interval Construction
radseq supports multithreading of FreeBayes through the bam_intervals_bedtools.nf subworkflow that uses a collection of BEDtools software and BEDOPS merge.
To enable the saving of files generated for interval construction in the output-folder set --save_bed_intervals=true.
For large datasets, it may be useful to randomly subsample the number of individuals going into bam_intervals_bedtools.nf subworkflow using --subset_intervals_channel=<integer>. Particularly at the BEDtools merge module the memory footprint can be large.
BEDtools bamtobed
Convert individual binary alignment files to bed format
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_bamtobed*.bed: individual bed file
BEDOPS merge
Merge individual bed files
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedops_merge*.bed: merged single bed file
BEDtools sort
Sort the single merged bed file based on reference index
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_sort*.bed: single sorted bed file
BEDtools coverage
Calculate number of reads across regions in a single individual bed file.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_coverage*.cov: Individual bed files with fourth column describing number of reads in a particular region
BEDtools merge cov
Determine the sum of coverage across all regions and individuals.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_merge*.cov: single bed file with fourth column describing number of reads in a particular region
BEDtools makewindows
Split regions with more than --splitByReadCoverage into half the total read length.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_makewindows*_cov.low.stats: regions less thanmax_read_coverage_to_split*_cov.high.stats: regions equal to or greater than--max_read_coverage_to_split*.tab: regions from*_cov.high.statssplit to half their read length
BEDtools intersect
Joins and removes any sites overlapping in the single merged bed file with split regions.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_intersect*.bed: Final single bed file to be subsequently split
Create intervals
Splits bed files into regions for input to FreeBayes.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/bedtools_intersectmapped.*.bed: split bed file
Variant Calling
FreeBayes
FreeBayes is a bayesian genetic variant detector capable of genotyping SNPs, indels, MNPs, and complex events smaller than the length of short-read sequencing alignment.
By default radseq will output a single vcf joined from independent runs. To enable the outputting of VCF files based on regions passed to FreeBayes use --save_freebayes_intervals=true.
Output files
-
{outdir}/{method}/variant_calling/*.vcf.gz: Final VCF
-
{outdir}/{method}/variant_calling/intervals*_*.vcf.gz: unsorted VCF intervals*_sort_*.vcf.gz: sorted VCF intervals*_sort_*.vcf.gz.tbi: sorted VCF intervals tabix index
Quality Control and Visualization
FastQC
Output files
fastqc/*_fastqc.html: FastQC report containing quality metrics.*_fastqc.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report, tab-delimited data file and plot images.
FastQC gives general quality metrics about your sequenced reads. It provides information about the quality score distribution across your reads, per base sequence content (%A/T/G/C), adapter contamination and overrepresented sequences. For further reading and documentation see the FastQC help pages.
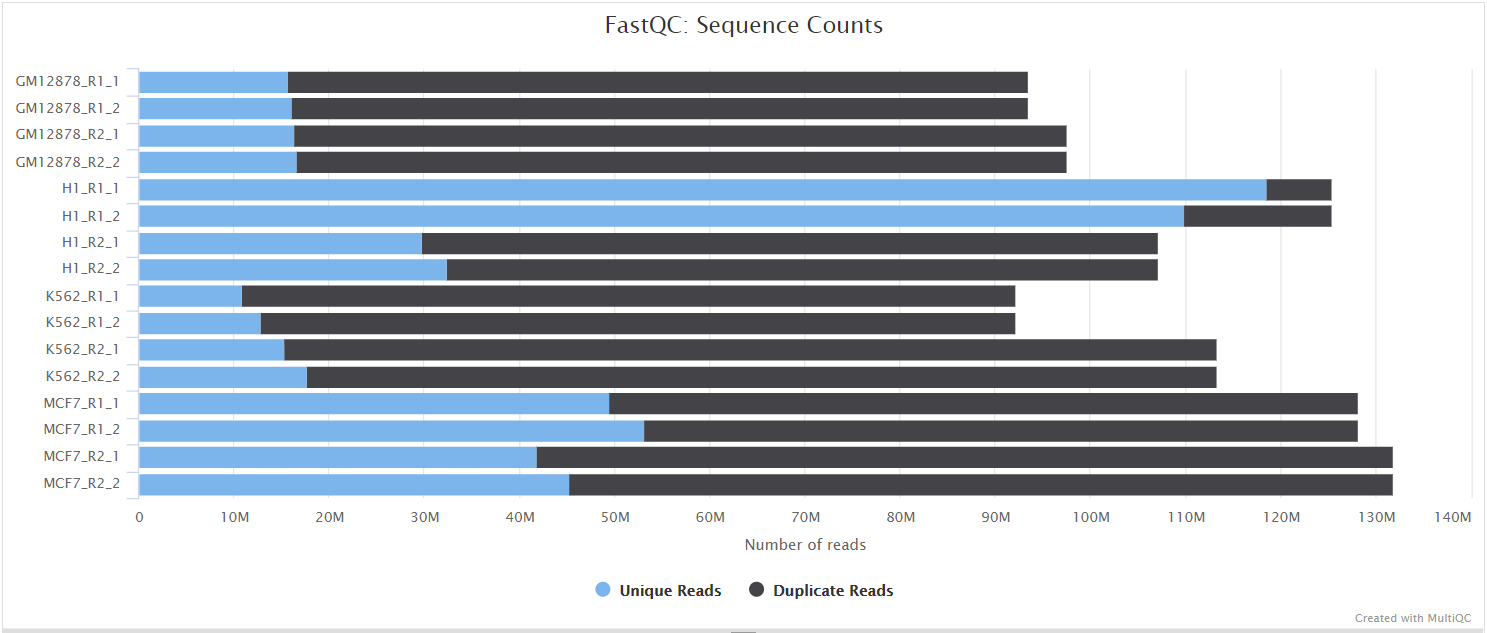
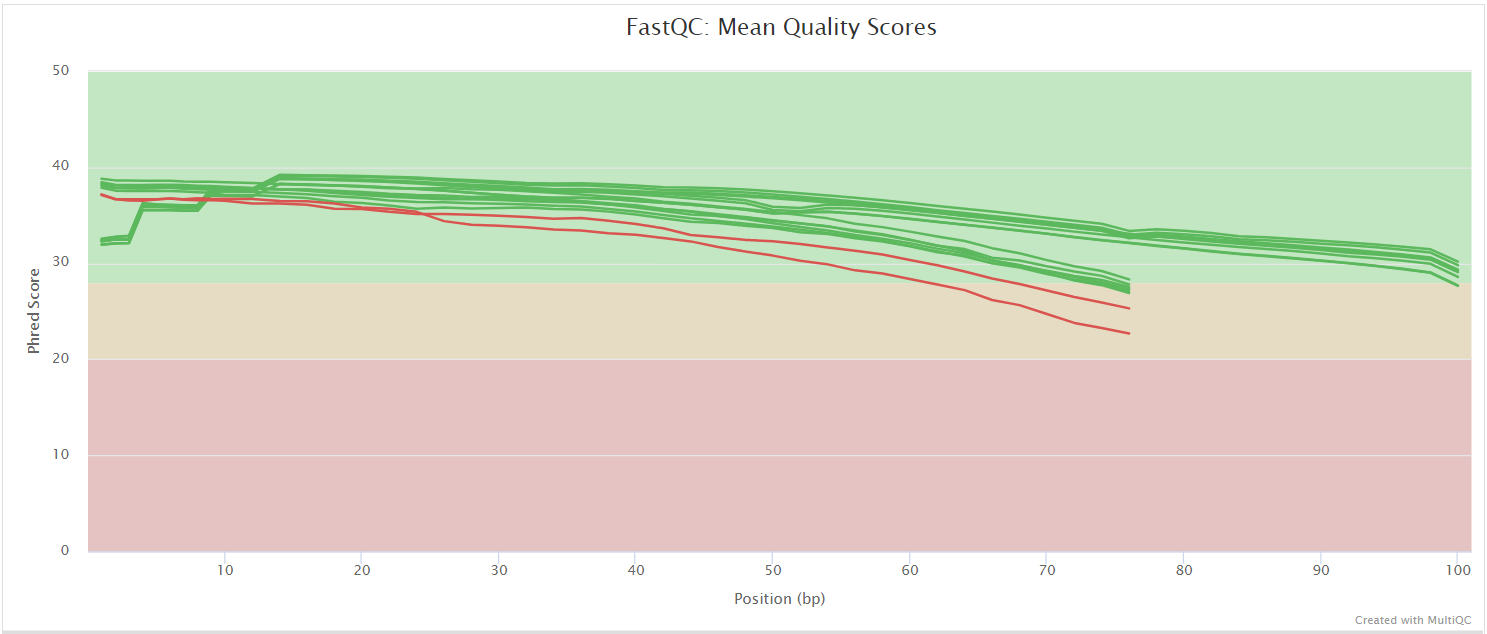
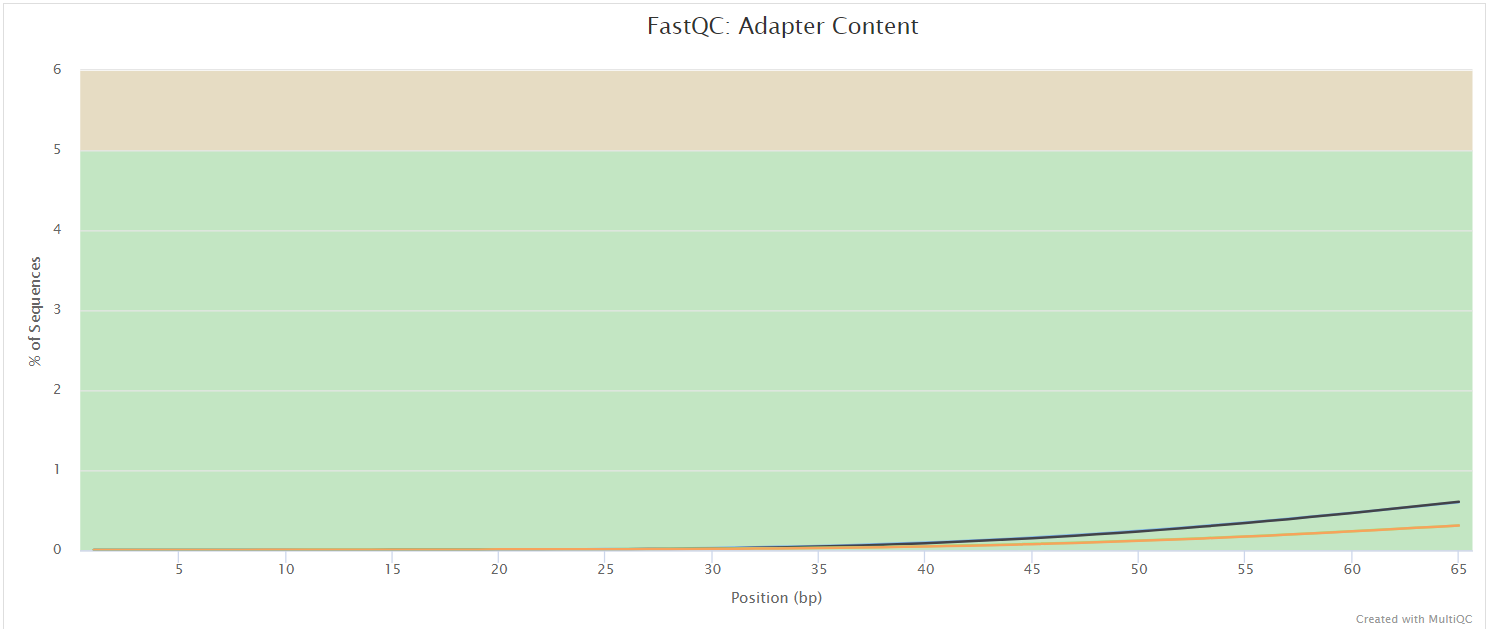
NB: The FastQC plots displayed in the MultiQC report shows untrimmed reads. They may contain adapter sequence and potentially regions with low quality.
FastP
FastP is a tool designed to be an all-in-one preprocessor for FastQ files. Statistics are passed to MultiQC.
Output files
{outdir}/fastp/*_fastp.html: Fastp report containing quality metrics*_fastp.log: Log output containing statistics
samtools
Alignment statistics may be generated from BAM files with samtools stats, samtools flagstat, samtools idxstats.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/alignments/{aligner}/samtools_stats{*.flagstat, *.stats, *.idxstats}- Statistics displayed in
MultiQC
- Statistics displayed in
bcftools stats
bcftools stats is a tool for collecting statistics from a VCF or BCF file that can be interpretted by MultiQC.
Output files
{outdir}/{method}/variant_calling/*_stats.txt:
MultiQC
Output files
multiqc/multiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.multiqc_data/: directory containing parsed statistics from the different tools used in the pipeline.multiqc_plots/: directory containing static images from the report in various formats.
MultiQC is a visualization tool that generates a single HTML report summarising all samples in your project. Most of the pipeline QC results are visualised in the report and further statistics are available in the report data directory.
Results generated by MultiQC collate pipeline QC from supported tools e.g. FastQC. The pipeline has special steps which also allow the software versions to be reported in the MultiQC output for future traceability. For more information about how to use MultiQC reports, see http://multiqc.info.
Pipeline information
Output files
pipeline_info/- Reports generated by Nextflow:
execution_report.html,execution_timeline.html,execution_trace.txtandpipeline_dag.dot/pipeline_dag.svg. - Reports generated by the pipeline:
pipeline_report.html,pipeline_report.txtandsoftware_versions.yml. Thepipeline_report*files will only be present if the--email/--email_on_failparameter’s are used when running the pipeline. - Reformatted samplesheet files used as input to the pipeline:
samplesheet.valid.csv.
- Reports generated by Nextflow:
Nextflow provides excellent functionality for generating various reports relevant to the running and execution of the pipeline. This will allow you to troubleshoot errors with the running of the pipeline, and also provide you with other information such as launch commands, run times and resource usage.